Windows patch management (or Windows patching process) involves updating and maintaining the Windows operating system and its related software applications to ensure security, stability and performance of Windows-based environment. Microsoft patch management encompasses the entire workflow, right from scanning and detecting the missing patches to downloading, testing & approving the patches and finally deploying them to the required systems in the network. With servers playing a critical role, Windows server patching is vital in bolstering the network security of your enterprise. Windows server patching is the process of installing and patching all the servers in your IT environment.
The Windows patch management process also includes generating reports of the deployment process for audits and compliance purposes. A well-organized Windows patch management strategy can significantly reduce the exposure to security risks and maintain a secure Windows-based environment. Using a patch management solution, the entire Windows patching process can be automated, so that admins don't need to go around to every computer and manually check whether all missing patches were identified and deployed. The Windows patch management software also generates reports for you to confirm if the Windows patches have been deployed properly.
Microsoft releases security updates for all of its products on the second Tuesday of every month known as the Patch Tuesday. With a plethora of patches being released this week, it can be crucial for admins to prioritize the patches and then deploy them to the systems.
Here are some of the best practices that you can follow to perform Windows patching in your network:
Microsoft assigns severities for the patches released, based on how severe the vulnerabilities are. These can range from Critical to Low and Unrated in some cases. Before deploying the Windows patch, it is crucial to prioritize them based on the severity.
For example, Critical and High severity patches should be deployed urgently. Patches of lesser severity can then be prioritized based on the regular patching schedules.
While regular Windows patch management is of paramount importance, it is highly recommended to test the patches before deploying them to the systems. In case the patches aren't tested for bugs/functional correctness, they can cause system downtime and employee un-productivity in the enterprise network.
Deploying a Windows patch across the multitude of endpoints in the network can be challenging. However, to ensure a correct balance between employee productivity and network security, admins should create broad deployment windows spread over multiple days/weeks.
This helps in streamlining Windows patching in the network as the broad window allows all the systems to be properly patched.
Many a time, patch deployment can fail for certain systems due to inactivity or network issues. Not only does this affect system compliance but can also pave the way for critical vulnerabilities to exploit the systems.
Hence, it is highly recommended to generate patch deployment reports for a holistic view of the network's patch status. This further makes it easier for admins to detect the unpatched systems and re-deploy the patches to them.
Microsoft Windows is the most widely-used operating system. With frequent security patches and updates released, manually applying the Windows updates to all the endpoints in a network can be a headache.
What's more? Deploying Feature Packs in particular can be tricky across several endpoints, given their large sizes. To simplify the Windows patching process, you can use patch management software such as Patch Manager Plus to deploy patches across your enterprise's network automatically. This creates a consistently configured environment that is secure against known vulnerabilities found in Windows and all other applications.
If you're looking for end-to-end Windows patch management software, Patch Manager Plus checks all the boxes. It handles every aspect of Windows patch management, right from detecting and installing Windows updates, hotfixes, rollups, security updates, etc. to defending the Windows-based systems by testing patches before rolling them out to the production environment to ensure they don't cause any issues.
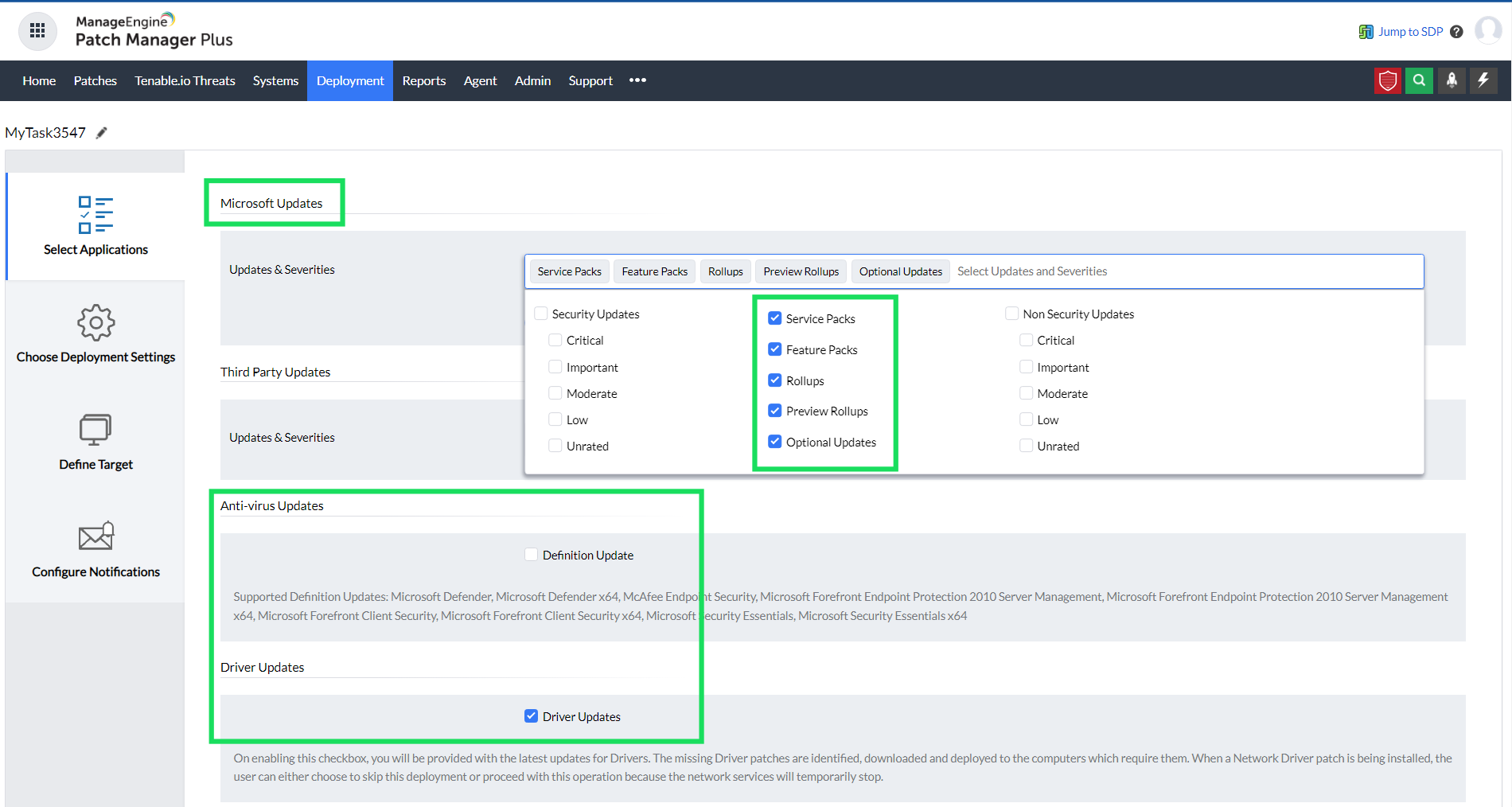
Not just updates for Windows, Patch Manager Plus also supports patching for over 850 third-party applications, antivirus definitions, and driver updates.
In addition to Windows computers and workstations, this solution, also lets you perform Windows server patch management. Right from a centralized console, this Windows patch management software detects the missing Windows server patches and deploys them to the required systems.
Patch Manager Plus' Windows patch management software features:
Patch Manager Plus supports the installation of Feature Packs for Windows OS. Each Windows 10 update comes with a lot of new features and enhancements to make a user's life easier. Patch Manager Plus automatically installs any dependency files before installing a Feature Pack.
If you're running Microsoft Forefront Client Security, Microsoft Defender, or any other antivirus on your network's computers, you can automate the antivirus definition updates with Patch Manager Plus. The Automate Patch Deployment (APD) functionality helps you schedule the frequency of scanning and updating the antivirus definitions in the systems.
Rollup updates are a cumulative setup of hotfixes that contains security updates and critical updates that need to be deployed immediately. In addition to Feature Packs, Quality Updates, and Optional Updates, admins can also deploy Rollups to the systems, right from the Patch Manager Plus console.
Patch Manager Plus' Windows patch management feature supports the following versions:
When it comes to Windows server patching, here are the supported Windows Server operating systems:
Patch Manager Plus automates the entire Windows patch management process with its Automated Patch Deployment (APD) feature. You can also view the System Health Status, based on the number of missing patches by using this Windows patch management tool.
Managing your Windows patching with Patch Manager Plus works for both Active Directory-based and workgroup-based networks. In addition, network managers can completely automate their Windows patch management routine with just a few clicks, right from a centralized console.
Patch Manager Plus' Windows patch management feature adds the following advantages to your network:
Saves time and money: With the Automate Patch Deployment feature, the entire Windows patching process is automated, right from scanning for and deploying patches, to generating patch status reports.
Bolster your network's security: Most cyberattacks leverage known vulnerabilities to steal data and cause disruptions. Patching the known vulnerabilities as well as zero-days promptly further strengthens the security of your network.
Deploy the most up-to-date patches: Not just to thwart vulnerabilities, it is important to keep your Windows machines running with the latest Windows patches, so that you have access to the newer features and functionalities.
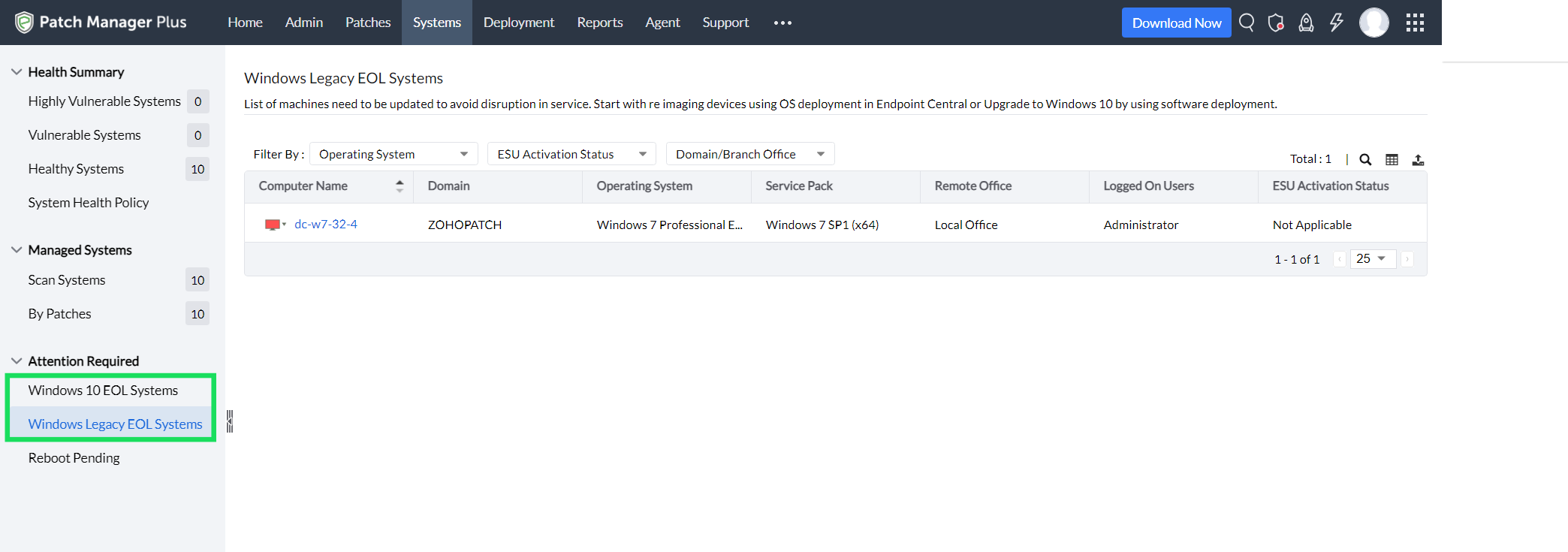
Detect, upgrade, and secure EOL systems: End-of-life systems pose a high risk to the security of the network, primarily because of the lack of security updates.
With Patch Manager Plus' Windows Legacy EOL Systems, admins can detect the legacy (EOL) systems in the network and can either upgrade them to the latest versions or take precautionary measures to safeguard them.
Windows Server patching: While patching on a Windows server can be more challenging than for other systems, Patch Manager Plus lets you seamlessly achieve this with its wide patching support for the Windows Server operating systems. In addition, the Self Service Portal for patches coupled with the flexible deployment policies ensures minimal downtime with maximum patching capability.
To perform Windows patch management using Patch Manager Plus, follow the steps below:
Windows patch management software is a specialized patch management solution that streamlines the process of identifying the missing Windows patches in your network, testing, approving and deploying them to the required systems.
Windows Update refers to the process of applying the latest Windows Feature Packs, Cumulative Updates, Rollups, and all other updates to the Windows systems.
Patch Management, on the contrary, is a broader term that encompasses the detection of missing patches in the systems, testing the patches, deploying them to the required systems, and generating reports for audits and compliance. This includes patches for Windows, Mac, Linux operating systems, and other third-party applications.
Windows patching has manifold benefits for the systems in the network. Some of the benefits are as follows:
Windows patches are updates released by Microsoft to fix an existing vulnerability in the Windows operating system or to add newer features to it. Microsoft releases security patches on the second Tuesday of every month, known as the Patch Tuesday. The other non-security patches are usually released in the first week of the month. In case of critical updates (for zero-days or critical vulnerabilities), Microsoft releases out-of-band patches.