Threat detection with Log360 across the length and breadth of your network
Adopt an effective and quick threat detection technology for your entire network to combat different types of threats.
Every organization needs a fast-acting, effective threat detection and incident response plan to counteract the numerous threats in today’s cybersecurity landscape. Log360, ManageEngine’s SIEM solution with integrated DLP and CASB capabilities, detects threats across the length and breadth of an enterprise network, covering endpoints, firewalls, web servers, databases, switches, routers and even cloud sources.
See how Log360 performs the three major types of threat detection―security event threat detection, network threat detection and endpoint threat detection, below.
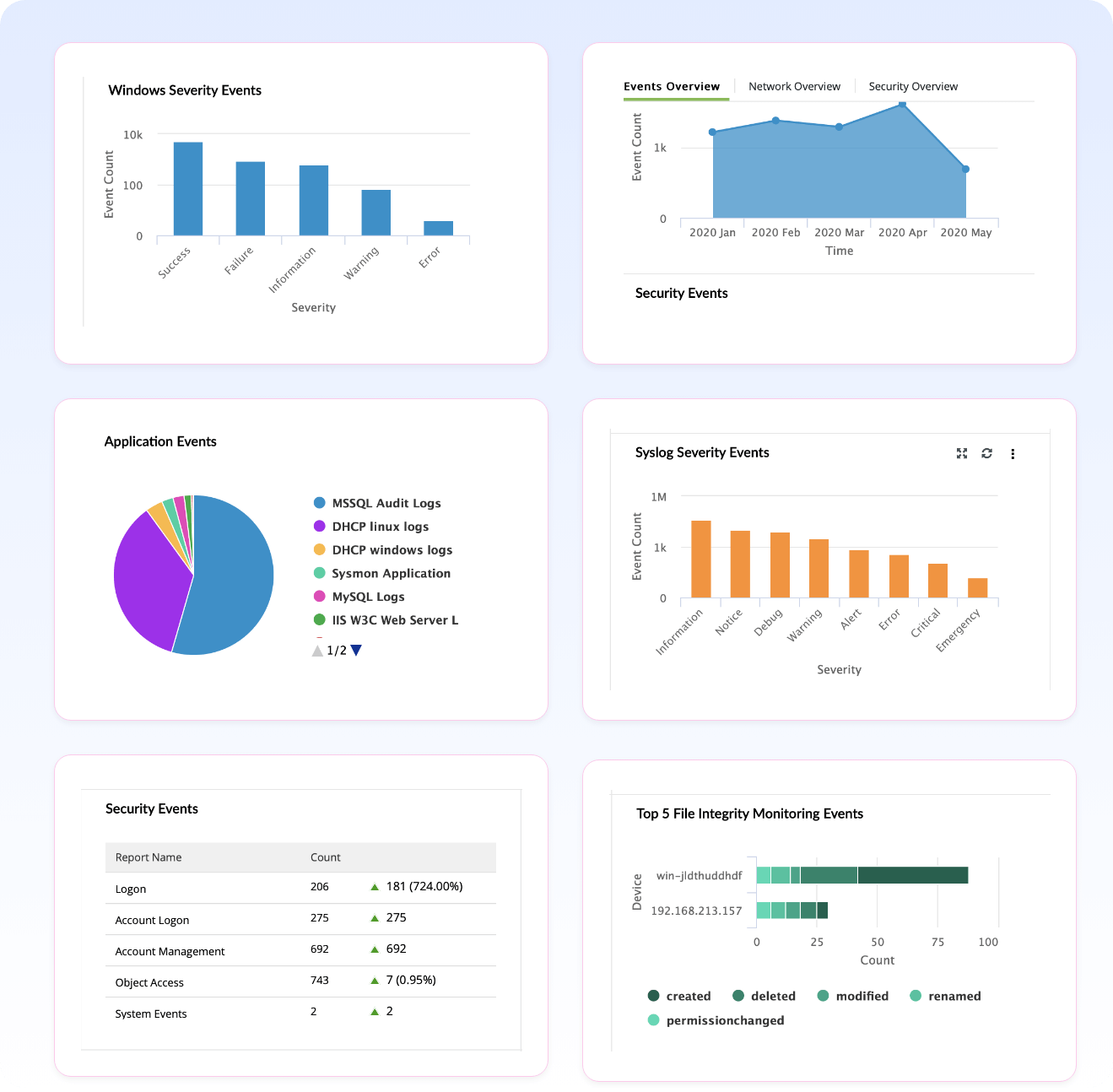
Security event threat detection
Events such as authentication, network access, and other critical errors and warnings, are termed security events. The threats that can be detected through these events are classified as security event threats. Some examples of security event threats include brute-force attacks, privilege misuse, and privilege escalation.
How Log360 detects security event threats
- Privileged user monitoring: Audit privileged user logons, logoffs, resource access. Spot unusual user activity and user-based threats using ML-based user and entity behavior analytics.
- Privilege escalation detection: Monitor user activities and detect privilege escalations and attempts to abuse privilege using signature-based MITRE ATT&CK technique implementation.
- Authentication failure monitoring: Investigate suspicious authentication failures on critical systems using security analytics dashboard and incident timeline detect and preempt brute force or unauthorized network access attempts
- Unauthorized data access detection: Monitor access to databases and sensitive data on file servers. Get visibility into unauthorized data access through file integrity monitoring and column integrity monitoring and column integrity monitoring.
Network threat detection
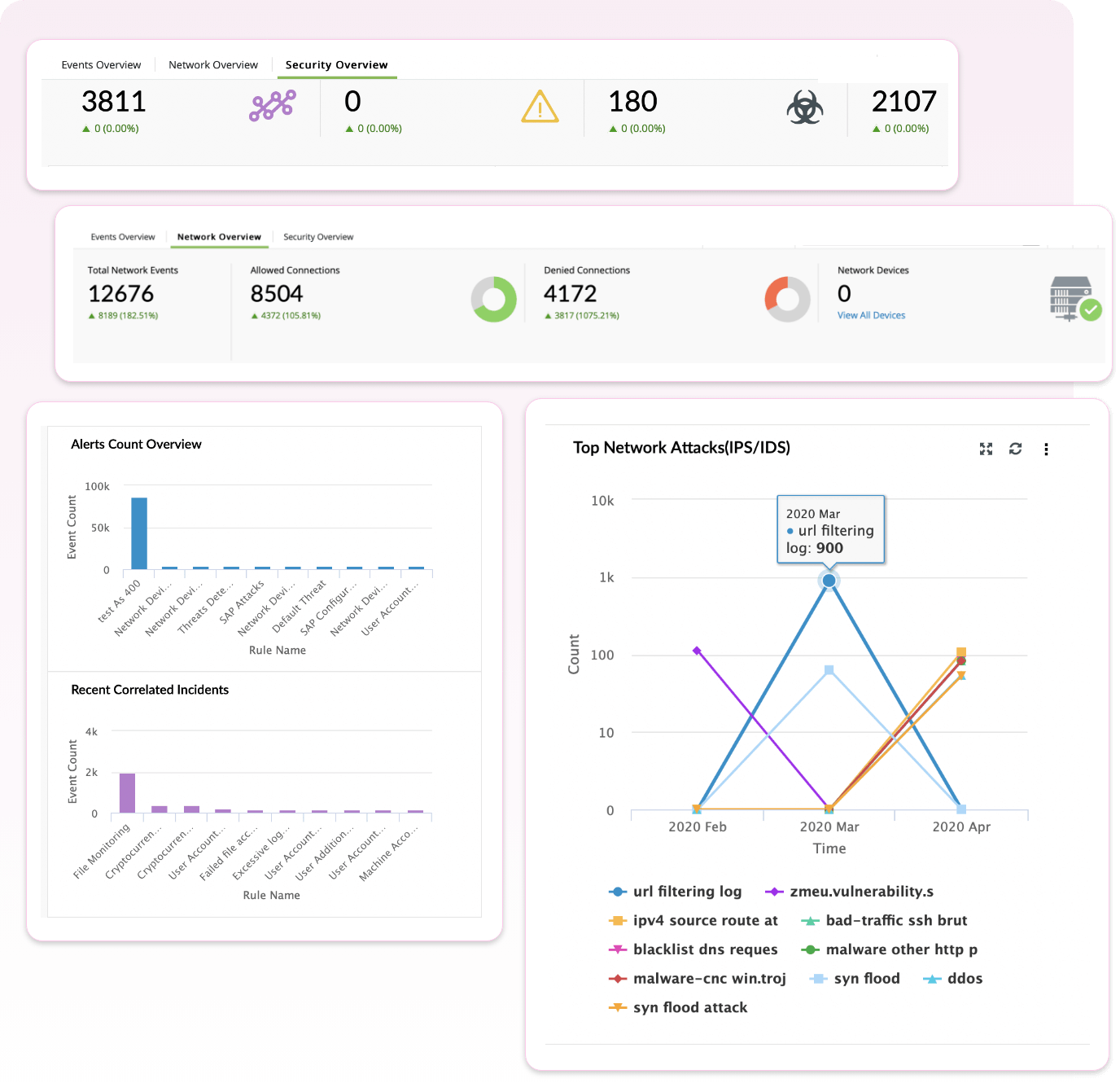
Network threats are unauthorized intrusion attempts into the network by an adversary to exfiltrate sensitive data or disrupt the network functioning and structure. Some examples of network threats include DoS, malware propagation, advanced persistent threats, data exfiltration, introduction of rogue devices and more. To detect these threats, it is necessary to understand and monitor network traffic.
How Log360 helps
- Traffic monitoring: Monitor network traffic for unusual, allowed and denied connections. Get insights into port activity to detect suspicious port usage.
- Change auditing: Monitor firewall policies to detect changes made by adversaries to accommodate malicious traffic.
- Auto-updated threat intelligence: Detect and stop malicious inbound and outbound traffic using dynamically updated threat feeds. Spot malicious IP addresses and URLs in network traffic and block them immediately.
- Rogue device detection: Spot rogue devices using search console and terminate them using incident response workflows.
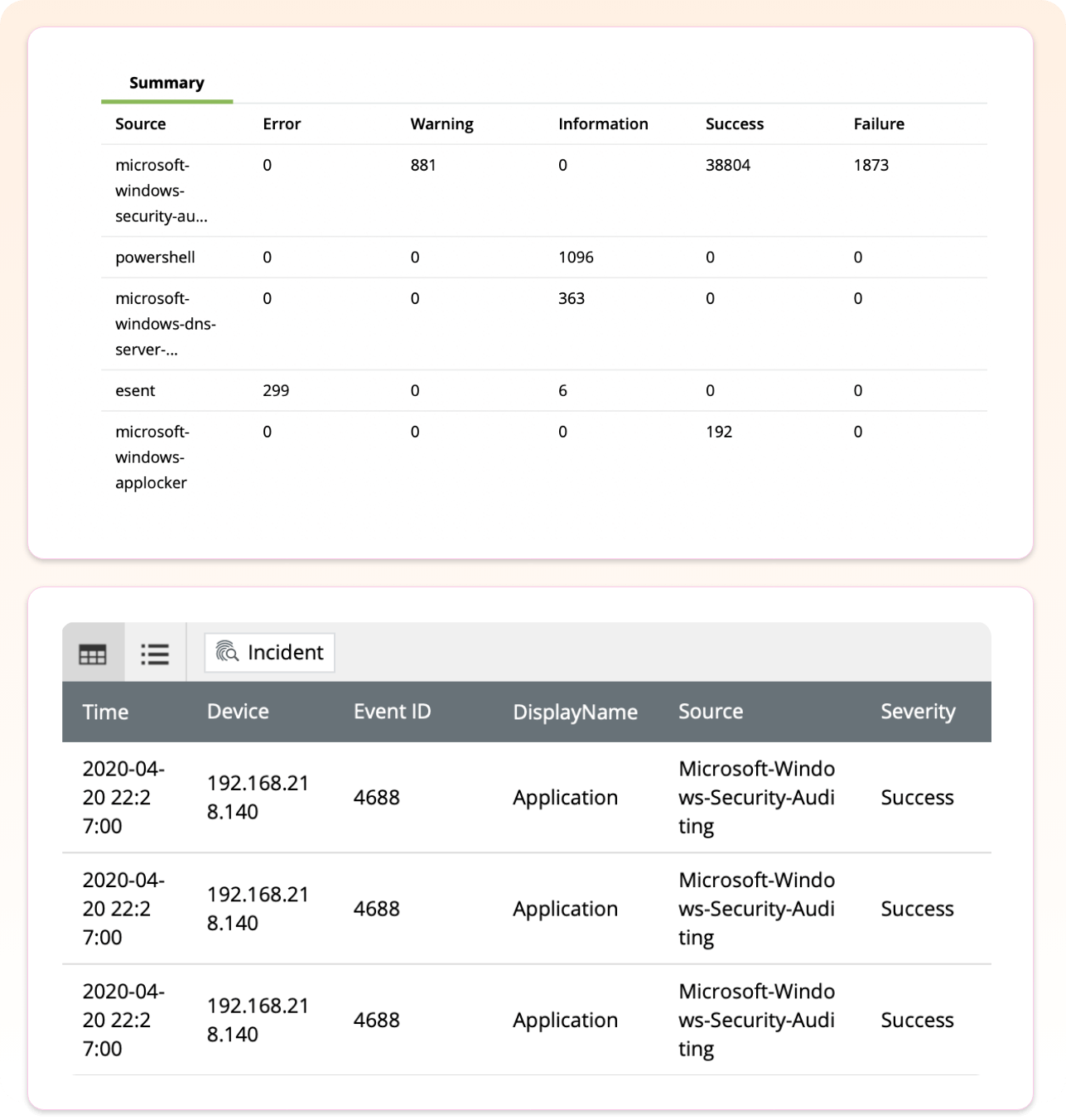
Endpoint threat detection
Threats often originate at endpoints. One example is ransomware, which sees huge profits year after year, by locking endpoints and demanding ransom for access. Other endpoint threats include unusual user behavior, device malfunction, misconfigurations, and suspicious downloads. These losses and damage can be largely limited with the help of timely intervention, which is possible with endpoint threat detection and response technology.
How Log360 helps
- Ransomware detection: Spot multiple ransomware strains well as generic ones through prebuilt correlation rules and real-time notification.
- Anomaly detection: Detect unusual user and entity behavior using ML algorithms.
- Malware detection: Identify malicious and suspicious software installations on Windows and Linux machines.
Why consider Log360 for threat detection?
-
Real-time incident detection
Real-time incident detection with built-in incident management as well as support for third party ticketing tools.
-
ML-based UEBA module
ML-based UEBA module that detects anomalies and facilitates risk-score based alerting.
-
Security dashboards for event monitoring
Security dashboards for event monitoring for both on premise and cloud log sources across the network.
-
File integrity monitoring
File integrity monitoring for critical system files and folders that monitors file access and modifications.
-
A powerful search engine
A powerful search engine that facilitates and threat hunting .
-
Automated workflows
Automated workflows for immediate incident response.
-
An auto-updated threat intelligence module
An auto-updated threat intelligence module that receives feeds from trusted sources.



