In our highly globalized economy, business networks are distributed across different continents. For instance, the development or production team's networks of a company may be in one country and the organization's headquarters may be in a different strategic location. A distributed architecture like this can increase production and operational costs, but these costs can be slashed by deploying effective, central communication channels. These channels help teams spread across different geographical locations collaborate efficiently.
This is why continuous communication between geographically distributed networks is vital for day-to-day business operations. It is essential that these networks communicate seamlessly to give the business a competitive edge in the market. But what if there's lag slowing down your network operations and reducing efficiency? The best solution to this problem is to measure your network's latency using powerful network latency monitoring software.
The process of tracking important metrics to avoid latency in network communication using a network latency monitoring tool is called network latency monitoring.
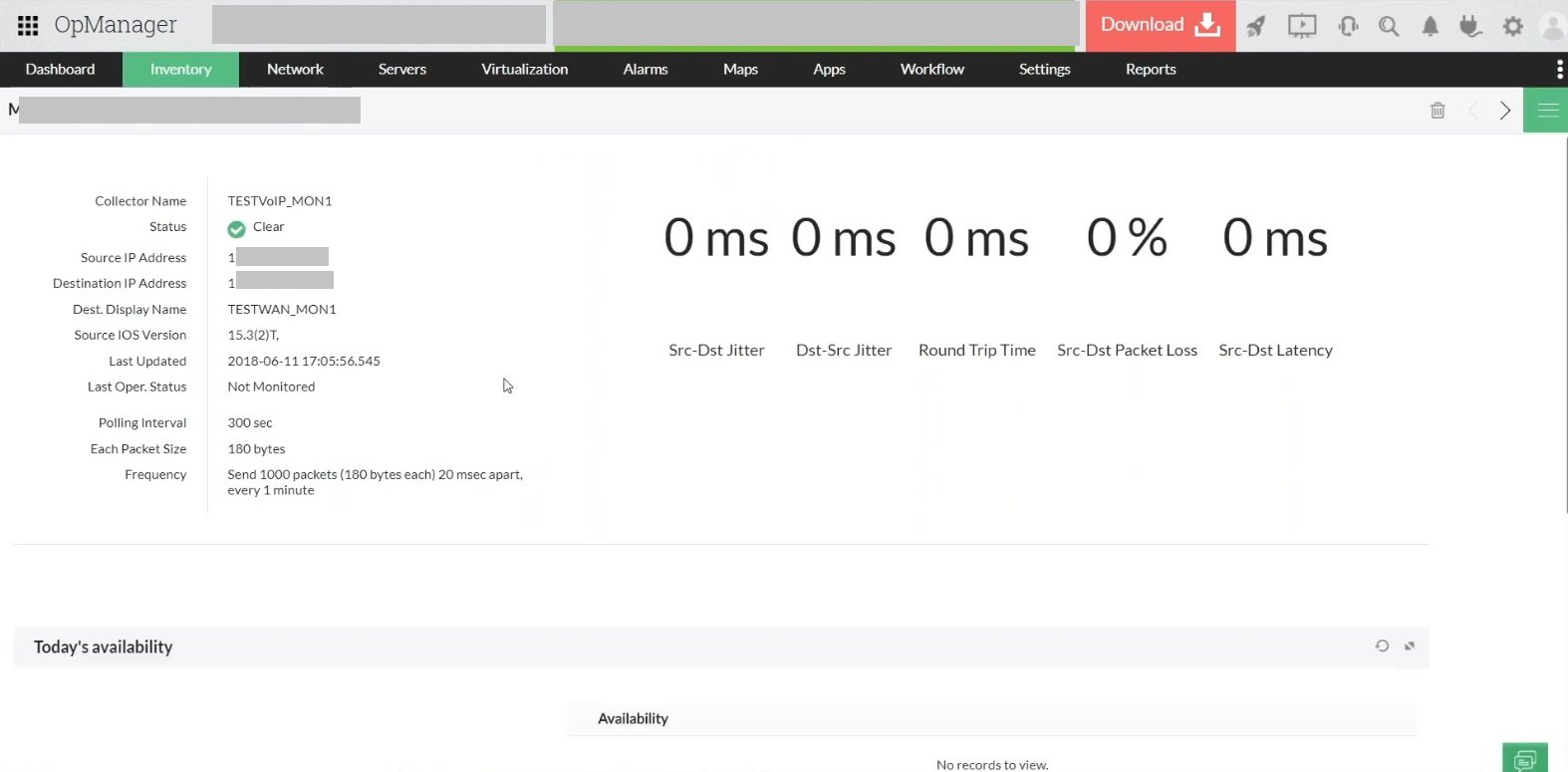
OpManager effectively performs network latency testing by tracking the total round-trip time (RTT) taken by data packets to reach the destination and travel back again.
Let's consider an example. Assume that your development center is located in India and your company's headquarters in Los Angeles. Both of these networks would be connected by a WAN link.
Monitoring the WAN link becomes crucial in this context to avoid latency issues.
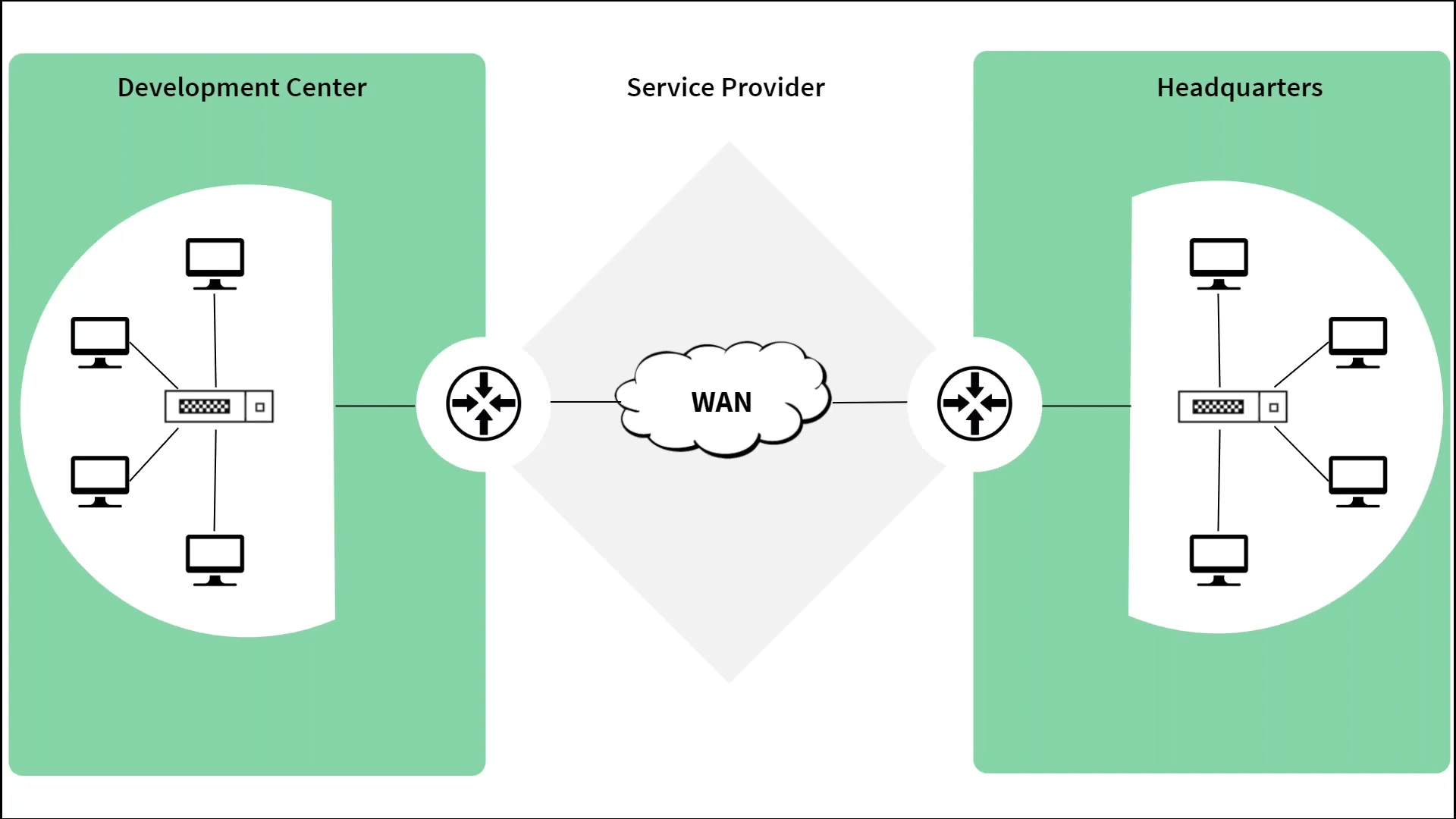
You can use OpManager's WAN monitoring feature as a network latency performance monitor to measure the following metrics.
The WAN RTT monitor in OpManager mitigates network latency by diagnosing the network paths with a high RTT and helps the IT admin to resolve poor WAN performance.
Monitor network latency using OpManger's WAN monitor. It identifies outages between two network stations by performing a traceroute action to get the required information on packet loss. This is how OpManager provides Packet Loss Monitoring. Furthermore, it provides a hop-wise view of the latency graph in a single window. This network latency monitor helps you drill down and precisely locate the hop at which the outage occurred.
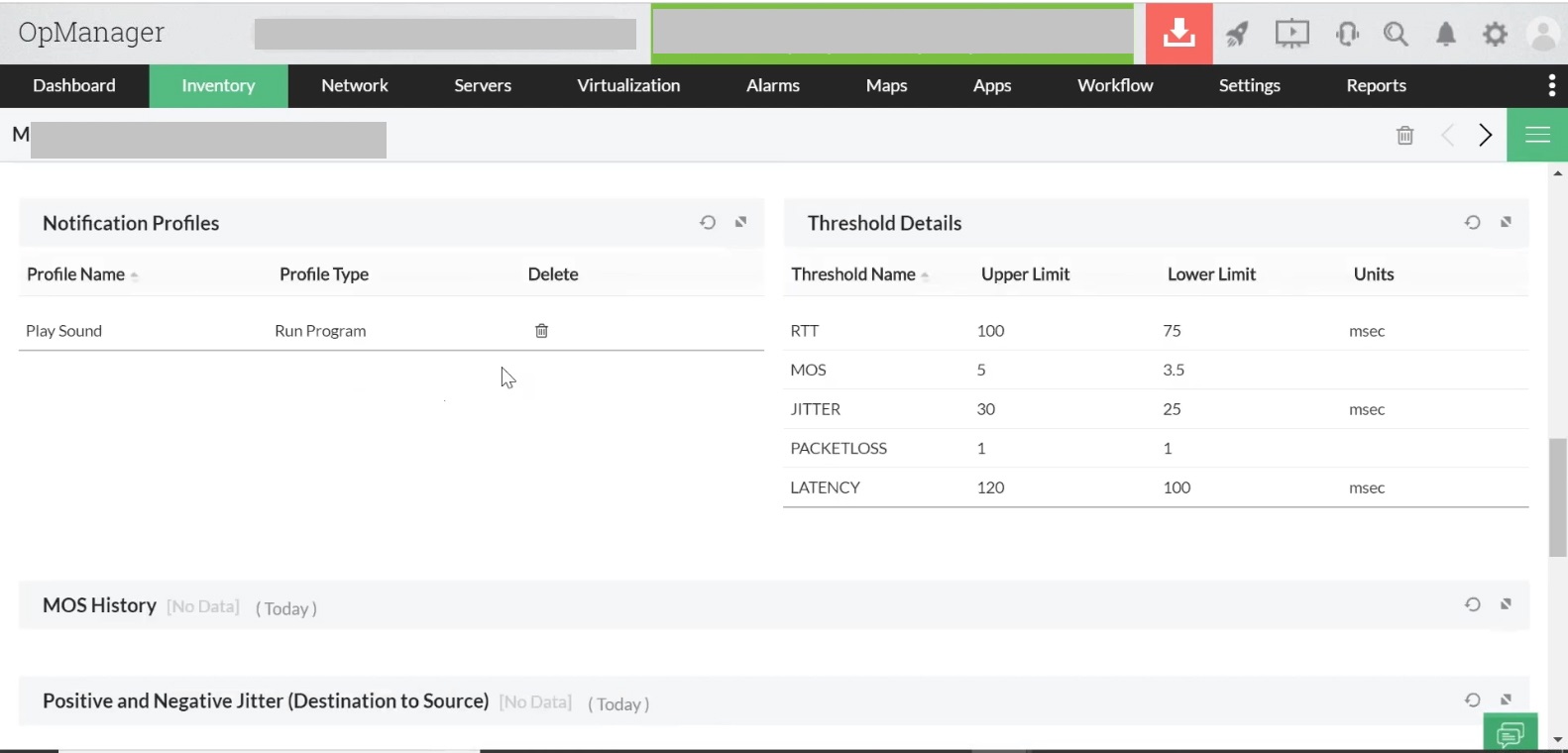
Use the WAN monitoring feature in OpManager to configure threshold values for RTT .
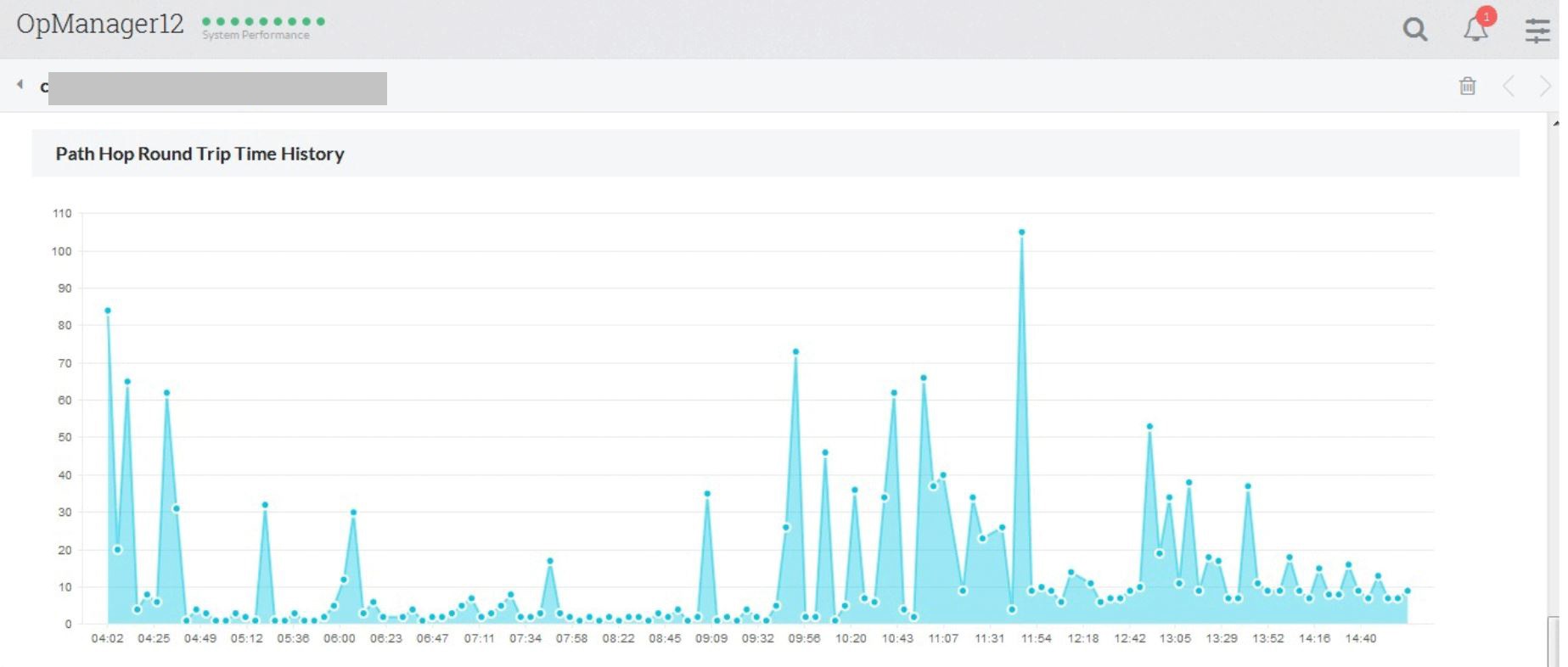
You can also use reports to obtain information about threshold violations with graphical representations. This helps you to make informed decisions and avoid network latency. You can see the WAN RTT historical trend report in the image below.
Many organizations use Voice over Internet Protocol (VoIP) for communication due to its functions and low cost.
That said, there are operational constraints that cause latency issues resulting in a communication lag. As an IT admin you can use OpManager as a network latency test tool and monitor VoIP calls to make sure that the quality of the call is maintained at an optimum level for comfortable conversations. The VoIP monitor in OpManager allows you to see the level of latency and packet loss occurring in your network.
If voice calls are a priority to your business, then you can effectively track the following metrics using ManageEngine OpManager.
Jitter
Jitter determines the quality of the communication and it is defined as a deviation from the average latency value. Ideally the deviation should be as low as 20 to 25 milliseconds.
Latency
Latency refers to the total time for the data packets to reach the recipient device. The recommended value for latency is 125 milliseconds. Setting a threshold less than 125 milliseconds will notify the network administrator and help avoid latency.
Packet loss transmission
Packet losses during transmission can interrupt communication between two networks. A packet loss of 5 percent is permissible in this case.
Mean opinion score (MOS)
The MOS is the average of different parameters like latency, jitter, etc. The MOS ranges from 1-5. A higher number indicates better quality.
Latency in VoIP-based networks is primarily caused due to configuration and bandwidth-related issues. Any irregularities caused on the VoIP network will lead to packet loss, which eventually disrupts the quality of communication.
The VoIP gateway establishes the connection between a traditional phone and a communication device on the VoIP network. Now, if the gateway is not configured properly, it may reduce the call quality by causing a lag in communication.
If your internet provider fails to provide the agreed upon bandwidth, then it might result in packet loss. This breaks the communication and you will not be able to receive all the information from the sender.
OpManger's VoIP monitor helps the network administrator locate latency issues and quickly resolve them before they become critical.