

As an administrator, many a time you would have felt mundane routines spill over crucial attention-seeking jobs of your network. Endpoint Central answers this concern through its User & Role Management module; delegating routine activities to chosen users with well-defined permission levels. You can easily administer the users, and define their scope to manage a specific set of computers.
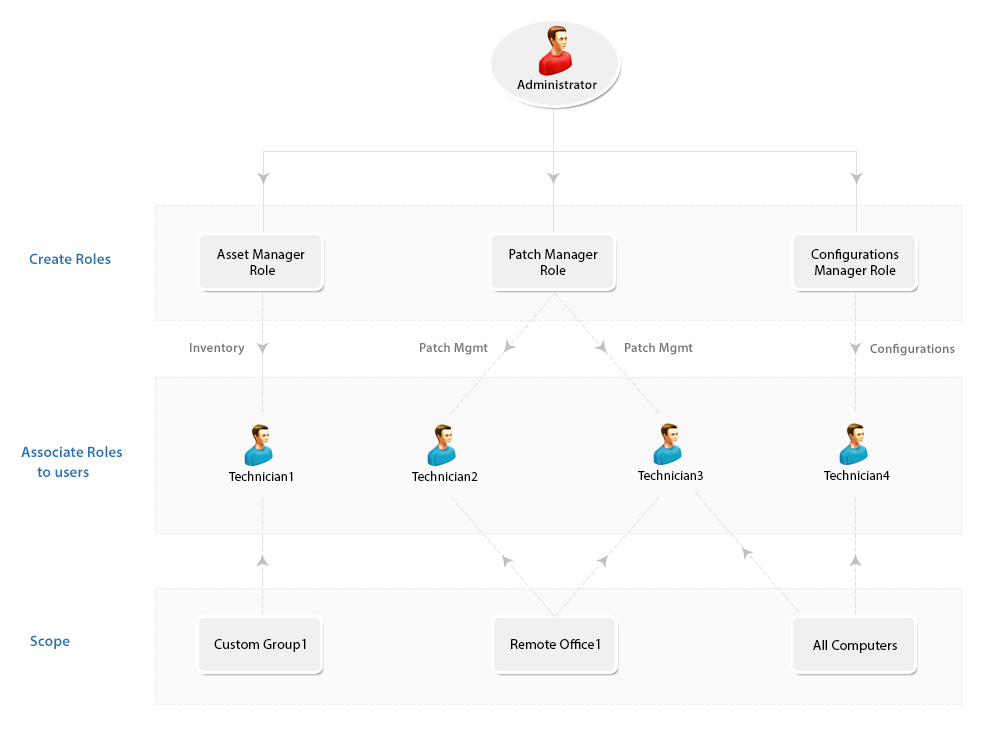
Some of the most commonly used Roles are specified under Pre-defined Roles. However, you also have the flexibility to define roles that best suit your requirements under the User-defined Roles and grant appropriate permissions. Here's a brief on the Pre-defined and User-defined roles respectively:
You can tailor-make any number of roles, and give them permissions based on your personalized needs. These customized roles fall under the User-defined category. For a better understanding let us quickly see how to create a User-defined Role in the following section.
Follow the steps mentioned below to create a new User-defined role:
1. Select the Admin tab and click User Administration under Global Settings. This opens the User Administration page.
2. Select the Role tab and click the Add Role button.
3. Specify the Role Name and a small description about it.
4. You can define module-wise permission level for the Role in the Select Control Section.
The permission levels are broadly classified into:
Full Control - To perform all operations like an administrator, for the specific module
Write - To perform all the operations, except few restrictions as explained in this table
Read - To only view the details in that module
No Access - To hide the module from the User (For more details, refer the user role and permission table.)
5. Click Add button.
You have successfully created a new role.
The role you have just created will now be available in the Roles list of the user creation module. Role deletion cannot be performed if that role is associated even with a single User. However you can modify the permission levels for all User-defined roles.
You will find the following roles in the Pre-defined category:
Administrator Role: The Administrator role signifies the Super Admin who exercises full control, on all modules. The operations that are listed under the Admin tab include:
Guest Role: The Guest Role retains the Read Only permission to all modules. A user who is associated to the Guest Role, will have the privileges to scan and view various information about different modules, although making changes is strictly prohibited. Guest Role also has Read Only permission for viewing, MDM inventory details, reports, profiles and Apps of the mobile devices.
Technician Role: The Technician Role has a well defined set of permissions to do specific operations. Users under the Technician role are restricted from performing all the operations listed under the Admin tab. The operations that can be performed by users associated with the Technician Role include:
Auditor: The Auditor role is specially crafted for Auditing Purposes. This role will help you grant permissions to auditors view the details of software inventory, check for license compliance, etc. Users with "Auditor Role" can also have read permission for MDM Reports.
Remote Desktop Viewer: The Remote Desktop Viewer Role will allow the users associated with it to Invoke a Remote desktop connection and view details of users who had connected to a particular system.
IT Asset Manager: The IT Asset Manager has complete access to the Asset Management module and all the other features are inaccessible. IT Asset Manager can also view the Inventory details of all the Mobile Devices.
Patch Manager: The Patch Manager role has complete access to Patch Management. Patch Manager will also have the privilege to access and use "Tools", like Wake On LAN, Remote Shutdown, System Manager and ability to schedule Patch Reports. All the other modules/features are inaccessible.
Mobile Device Manager: Mobile Device Manager role has write permission for the following, Inventory, Reports, Profiles and Apps in Mobile Device Management.
OS Deployer: The OS deployer role provides the associated user the privilege to capture images of Windows OS and deploy it across the network computers.
Note: Learn more about User Roles and Permission Level.
Endpoint Central provides you the privilege of defining a scope for the users with which you can define the target computers, which can be mapped to every user. By limiting the user's permission to specific set of computers, you can feel assured that the user has enough permission to perform their roles and not excess permission to take unduly advantage.
The target that you define as the scope can be one of the following:
When the target is defined as 'All Computers', users will have permission to execute all the privileges defined in the role, to all the computers. Though the scope is all computers, the permission level is determined only by the role to which the user is mapped.
You can create specific custom groups for management purposes and associate it to the users. The custom groups that you create should be Unique, so that no computer can belong to more than one custom group. These are computer based custom groups which are created for user management purpose, is defined as "scope" for the user. Refer to this to know more about Creating Custom Groups
You can create specific remote offices or use the existing remote offices to be defined as the scope for the users. More than one user can have manage the same remote offices. Similarly more than one remote office can be mapped to the same user, however you cannot have a combination of remote offices and unique groups as a part of the scope.
More than one user can share the same scope. In such cases, configurations/tasks applied to the scope can be managed by more than one user. To know more, refer to this: Points to be noted
When a scope of the user is modified, the user will not be able to manage the configurations/tasks, which were created. The user will have permission to clone the configurations without the target to re-use them for the user's current scope. Modifying the computers within the scope will not be considered as modifying the scope.
Learn more on scope allocation for a newly created user
Note: This is applicable only after Endpoint Central build # 10.1.2211.1
For security reasons, mail server is required to send user activation links when creating new user accounts. If the mail server is not configured, navigate to Admin tab> Server Settings>Mail Server Settings to configure your mail server. Kindly go through this link to learn about configuring mail server.
You have successfully create a user and associated a role to the user with the scope of the computers that need to be managed.
When you opt to authenticate a user via Active Directory, the user should have privileges to login to the domain from the computer where the product Server is installed.
At times when you find a user's contribution obsolete, you can go ahead and delete the user from the User List. The user removed will no more exercise Module Permissions.
Enabling Two Factor Authentication will secure the access to the web console. Users will be prompted to enter the One Time Password (OTP) along with their default password. You can configure the settings to save the OTP for the specific browser. If this option is enabled, user will not be prompted for OTP for the number of days, specified here : Admin -> User Administration -> Two Factor Authentication. You can choose the mode for two factor authentication, which could be either via email or an authenticator app (Zoho OneAuth, Google Authenticator, MS Auth, DUO Auth, etc.)
One Time password will be sent to each user via email. You cannot enable Two Factor Authentication if one or more users do not have email address mapped with the product server. You should ensure that email address of all the users are registered with the product server.
When two factor authentication is enabled, users will receive an email with the details of the OTP. Every OTP is valid for 15 minutes from the time of generation. OTP will be an auto-generated 6 digit number. You can also allow the users to save the OTP on their web browsers. You should specify the number of days allowed for the OTP to be saved on the web browser. Users will not be prompted for OTP, if they choose to save the OTP on the browser. If you specify the number of days as 0, then users will not be allowed to save the OTP on the web browser. OTP will be generated every time the user tries to login into the web console.
Note: The Authenticator app could be Zoho OneAuth, Google Authenticator, MS Auth, DUO Auth, etc..
You can choose any of the above mentioned authenticator apps to generate an OTP. You should install the authenticator app on your smart phone.
Here are the download links to a few commonly used authenticator apps:
Download and install the authenticator app on your mobile device. When you login to the web console for the first time, a QR code will be displayed. You should open the authenticator app and scan the QR code to create an account for Endpoint Central. You can see Endpoint Central is now added to the authenticator app and OTP will be generated automatically. The chosen authenticator app can also be selected after enabling two factor authentication via email.
You can use the OTP generated in the authenticator app as a secondary authentication and login to the product.
If the user has deleted the Endpoint Central account on the authenticator app, then the user should contact the administrator to restore Two Factor Authentication using the same app. Administrator can re-send the QR Code to restore the authenticator app from here : Admin -> User Management -> Actions (Under the appropriate user) -> Re-send QR Code.
If the Endpoint Central administrator is not able to access the authenicator app, he/she can contact other administrators to send the QR code via e-mail. If there are no other administrators available, then follow the steps given in the document to disable two-factor authentication and then access the server.
TFA adds an additional layer of security when logging into the product, by requiring the user logging to provide the unique time-bound one time passcode(OTP) generated using Google Authenticator or sent as an SMS to your mobile number. This process improves authentication, thereby preventing unauthorized access of user data.
Note : This settings will be applied to all Zoho users.
You can impose the following restrictions on passwords for user accounts:
You can configure the password policy for user accounts, by imposing the following restrictions while creating a password: